Busy clinic week with several patients from aboard with a single question? Is there an Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS) treatment for pain? Is there treatment for EDS pain?

What is EDS?
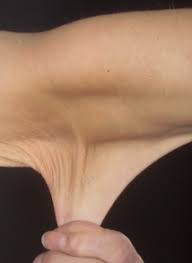
A group of inherited disorders that affect and weaken the connective tissues such as tendons and ligaments (1). Primary sites of involvement include skin, joint and blood vessels. Joints are typically hypermobile with excessive joint range of motion. Skin is also hyperextensible. The prevalence varies from region and some consider it to be as high as 0.75%-2%. (2). We have all seen such individuals whose flexibility seemed beyond normal.

Is EDS painful? Yes!!
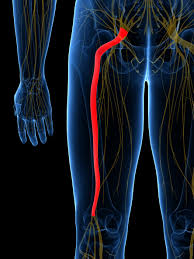
Overall, approximately 90% or more EDS patients suffer from chronic pain (3). Initially, most patients report joint pain as a result of traumas, dislocations, and sprains(4). The most common joints involved include the shoulder (80%), hands (75%) and knees (71%) (5). Compression of the nerves with resultant nerve pain is common and impacts approximately 68% of EDS patients (6).
Why is EDS Painful?
EDS is an inherited disorder characterized by a defect in collagen formation. Collagen is a major structural protein with many jobs which include formation of strong, tight bands of tissue to hold the body together. Defects in the collagen results in weakness in the supporting ligaments and tendons and increased laxity. Areas involved include joints, ligaments, skin, and tendons. Loose ligaments make joints susceptible to dislocation and injury to the cartilage and tendons. Nerves, arteries, and veins can also be irritated, compressed or damaged by the instability of the affected joints.
Does EDS cause muscle pain? Yes !!
Hypermobile joints place an additional stretch of the attached muscles resulting in pain, inflammation and possible injury.

Treatment options: improve joint stability & decrease pain
Chronic pain in patients with EDS is typically due to mechanical irritation or damage to the joint, tendon, ligament and nerve (7). Depression, psychological distress and sleep disturbances are common comorbidities. Anxiety and panic disorders have a high prevalence of EDS patients. (8) Treatment recommendations vary significantly but focus on joint stability and the prevention of joint and muscle injury. Physical therapy is key for the stability of a given joint. Bracing is another option to enhance joint stability.
Can instability be treated with injections? Yes!
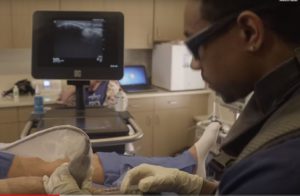
Yes! At the Centeno-Schultz Clinic, we have extensive experience in the management and treatment of patients with EDS. The ligaments and tendons of a given joint are critical to the stability of that joint. In the shoulder, for example, this would include the superior, middle and inferior glenohumeral ligaments. All these ligaments can be visualized and injected at the Centeno-Schultz Clinic. Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) or bone marrow concentrates are injected under precise ultrasound guidance into the loose or injured ligament or tendon in an effort to provide healing and strengthening.
Key Point
EDS is an inherited disorder with multiple manifestations and pain as a result of a defect in collagen formation. Loose ligaments and compromised tendons predispose joints to dislocation and trauma. EDS pain can be treated with precise ultrasound-guided injections of PRP or bone marrow concentrates. If you or a loved one suffers from EDS pain consider a consultation at the Centeno Schult Clinic where modern regenerative techniques utilizing ultrasound and x-ray guided PRP and stem cells injections are transforming the EDS world.
———–
References:
(1) Zhou Z, Rewari A, Shanthanna H. Management of chronic pain in Ehlers-Danlos syndrome: Two case reports and a review of literature. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018;97(45):e13115. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000013115
(2) Hakim AJ, Sahota A. Joint hypermobility and skin elasticity: the hereditary disorders of connective tissue. Clin Dermatol. 2006;24(6):521-33.DOI: 10.1016/j.clindermatol.2006.07.013
(6) .Chopra P, Tinkle B, Hamonet C, et al. Pain management in the Ehlers-Danlos syndromes. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 2017;175(1):212-9.DOI: 10.1002/ajmg.c.31554
(7) Chopra P, Tinkle B, Hamonet C, et al. Pain management in the Ehlers-Danlos syndromes. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 2017;175(1):212-9.DOI: 10.1002/ajmg.c.31554
(8) Bulbena A, Baeza-Velasco C, Bulbena-Cabré A, et al. Psychiatric and psychological aspects in the Ehlers-Danlos syndromes.Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 2017;175(1):237-45.DOI: 10.1002/ajmg.c.31544