Physical therapists often recommend specific exercises to alleviate shoulder pain, recognizing their effectiveness in both treating and preventing shoulder issues. These exercises, designed to enhance strength, flexibility, and mobility, can be a key component of a pain management strategy.
Moreover, the ability to perform these exercises at home makes them a convenient option for patients seeking pain relief. This approach empowers individuals to actively participate in their recovery, providing a non-invasive solution to shoulder pain that complements traditional medical treatments.
How to Prevent Shoulder Pain
Preventing shoulder pain involves recognizing those at risk—individuals engaged in repetitive arm and shoulder movements, athletes, and those with jobs demanding physical labor.
To reduce risk, incorporating regular shoulder-strengthening and flexibility exercises, maintaining proper posture, and using ergonomic tools and techniques are key.
Additionally, listening to one’s body and seeking early intervention for minor pains can prevent them from escalating into more severe conditions.
How Shoulder Exercises Can Relieve Pain
Shoulder exercises offer a viable non-surgical alternative for alleviating shoulder pain by addressing the root cause without the need for invasive procedures. These exercises help in regaining mobility, ensuring that the shoulder can move more freely and with less discomfort. They are crucial for recovering from injuries by strengthening the muscles around the shoulder, promoting faster and more effective healing.
Additionally, consistent practice of these exercises can stave off the need for surgery by improving shoulder health, reducing pain, and increasing function, thus offering a preventive approach to more severe shoulder issues.
Shoulder Conditions That Benefit from PT-Recommended Exercises
Shoulder exercises are beneficial for a range of conditions, impacting different parts of the shoulder. The most common shoulder conditions that benefit from physical therapy exercises are:
Shoulder Tendonitis
Physical therapy (PT) exercises for shoulder tendonitis typically focus on strengthening the muscles around the shoulder joint while also improving flexibility and range of motion. Exercises may include gentle stretching, resistance band exercises, and gradually increasing weight-bearing exercises to promote healing and prevent further inflammation.
Shoulder Bursitis
PT exercises for shoulder bursitis aim to reduce inflammation and improve shoulder stability. This may involve a gentle range of motion exercises, strengthening exercises for the muscles surrounding the shoulder joint, and modalities such as ice and heat therapy to decrease pain and swelling.
Osteoarthritis of the Shoulder
Physical therapy for osteoarthritis of the shoulder focuses on improving joint mobility, strengthening muscles to support the joint, and reducing pain and inflammation. Exercises may include gentle stretching, low-impact aerobic exercises, and resistance training to improve muscle strength and joint function.
Muscle Strain
PT exercises for muscle strains aim to promote healing, reduce pain, and restore normal function. This may involve gentle stretching exercises, progressive strengthening exercises, and functional activities to gradually reintroduce the injured muscle to normal activities.
Impingement
Physical therapy for shoulder impingement typically includes exercises to improve shoulder blade and rotator cuff muscle strength, as well as stretching exercises to improve flexibility and reduce compression on the shoulder tendons during movement.
Herniated Disc
PT exercises for a herniated disc in the shoulder may focus on improving posture, strengthening the muscles surrounding the shoulder and spine, and improving flexibility to reduce pressure on the affected disc and alleviate symptoms.
Arthritis
Physical therapy for arthritis aims to improve joint mobility, reduce pain, and increase strength and flexibility. This may involve a combination of exercises to improve range of motion, strengthen muscles, and stabilize the joint, as well as modalities such as heat and cold therapy to manage pain and inflammation.
Frozen Shoulder
Physical therapy for frozen shoulder aims to gradually restore range of motion and reduce pain and stiffness in the shoulder joint. This may involve gentle stretching exercises, manual therapy techniques to mobilize the joint, and progressive strengthening exercises to improve shoulder stability and function.
Rotator Cuff Tear
PT exercises for a rotator cuff tear focus on strengthening the muscles of the rotator cuff and shoulder girdle, improving shoulder joint stability, and gradually increasing range of motion. This may involve targeted strengthening exercises, manual therapy techniques, and functional exercises to restore normal shoulder function.
Other Injuries
PT exercises for other shoulder injuries will vary depending on the specific nature and severity of the injury.
However, common goals of physical therapy include reducing pain and inflammation, promoting healing, restoring normal function, and preventing future injury recurrence. Exercises may include a combination of stretching, strengthening, and functional exercises tailored to the individual’s needs and abilities.
Exercise 1: Chest Expansion

Objective: Improve chest and shoulder flexibility.
Benefits: Enhances breathing, opens up chest muscles, and reduces shoulder tightness.
Instructions:
- Stand with feet shoulder-width apart; interlace fingers behind your back.
- Straighten your arms and lift them slightly, opening up the chest.
- Hold for 20-30 seconds, taking deep breaths.
Safety tips:
- Keep your neck relaxed and don’t overarch your back.
- Adjust the intensity by raising or lowering your hands.
Exercise 2: Side-Lying Rotation

Objective: Strengthen the rotator cuff muscles.
Benefits: Increases shoulder stability and reduces injury risk.
Instructions:
- Lie on your side with the lower arm bent for support, top arm at your side with elbow bent at a 90-degree angle.
- Keeping the elbow at your side, slowly rotate the forearm upward.
- Hold briefly, then return to the starting position.
Safety tips:
- Keep movements controlled, and avoid any pain.
- Ensure the elbow remains close to your side throughout the exercise.
Exercise 3: Neck Release
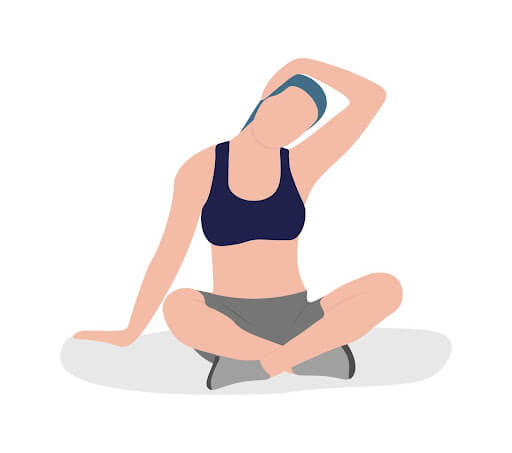

Objective: Alleviate tension in the neck and shoulders.
Benefits: Enhances neck mobility and reduces stress in shoulder muscles.
Instructions:
- Tilt your head towards one shoulder until a stretch is felt on the opposite side of your neck.
- Hold for 20-30 seconds.
- Repeat on the other side. Optional: Gently press with a hand for a deeper stretch.
Safety tips:
- Perform the stretch gently without forcing your head down.
- Keep the rest of your body relaxed, and avoid this exercise if it exacerbates any existing neck issues.
Exercise 4: Across the Chest
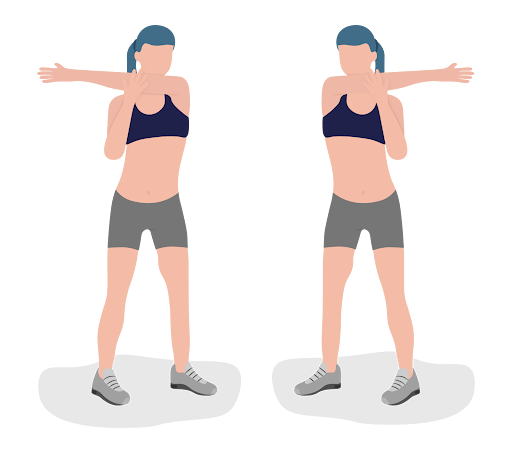

Objective: Stretch shoulder and upper back muscles.
Benefits: Relieves tension and increases flexibility in the shoulders.
Instructions:
- Bring one arm across your body at about chest height.
- Use the opposite hand to press the arm closer to your chest until a stretch is felt.
- Hold for 20-30 seconds, then switch arms.
Safety tips:
- Don’t press on the elbow joint or stretch to the point of pain.
- Keep your shoulders relaxed and down away from your ears.
Exercise 5: Pendulum
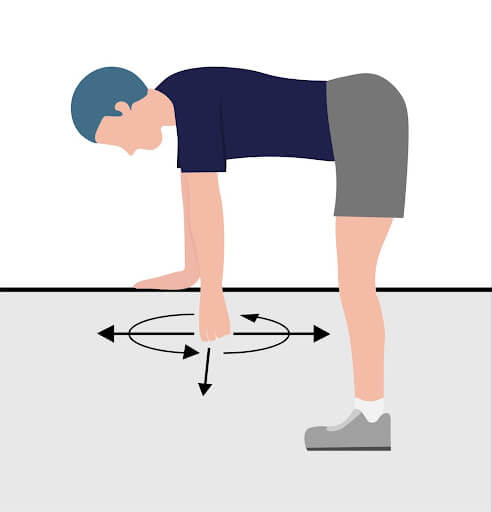
Objective: Improve shoulder mobility and decrease stiffness.
Benefits: Enhances circulation within the shoulder, promotes a gentle stretch in the muscles, and helps maintain or improve range of motion.
Instructions:
- Lean over, allowing the affected arm to dangle.
- Gently swing the arm in small circles, then gradually increase the motion as comfort allows, both clockwise and counterclockwise.
Safety tips:
- Keep movements gentle; avoid forceful swinging.
- If experiencing pain, discontinue the exercise.
Exercise 6: Doorway Stretch

Objective: Improve shoulder flexibility and stretch the chest to alleviate stiffness.
Benefits: Targets anterior deltoid, pectoral muscles, and biceps brachii for improved shoulder motion.
Instructions:
- Stand in a doorway, arms bent at 90 degrees, forearms against the frame.
- Lean forward until a stretch is felt in the chest and shoulders.
- Hold for 15-30 seconds, repeat 2-3 times.
Safety tips:
- Stretch to the point of mild tension, not pain.
- Keep your neck relaxed and aligned.
- Stop if you feel sharp pain.
Exercise 7: Downward Dog

Objective: Enhance shoulder strength and flexibility, offering a deep stretch to the whole body with a focus on the shoulders.
Benefits: This pose targets the entire shoulder girdle, especially the posterior deltoids, along with the spine, hamstrings, and calves, promoting overall flexibility and strength.
Instructions:
- Start on all fours, hands directly under shoulders, knees under hips.
- Lift your hips up and back, straightening your legs to form an inverted V shape.
- Press your hands firmly into the ground, stretching through your shoulders and back.
- Hold the position for 1-3 minutes, breathing deeply.
Safety tips:
- Keep your spine long and avoid locking your elbows.
- If you have wrist pain, try folding your mat for extra cushioning or use a wrist guard.
- Bend your knees slightly if your hamstrings are tight.
Exercise 8: Seated Twist
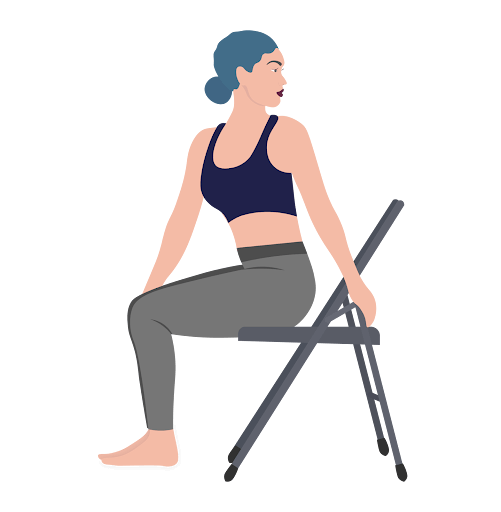

Objective: Targets shoulder mobility and aids in upper body flexibility.
Benefits: Primarily benefits the rotator cuff and scapular muscles by enhancing range of motion and relieving tension in the upper back and shoulder areas.
Instructions:
- Sit upright on a chair, feet flat on the ground.
- Place your right hand on the left knee and gently twist your torso to the left, looking over your left shoulder.
- Hold for 15-30 seconds, then switch sides.
Safety tips:
- Avoid twisting too far; the motion should be gentle and controlled.
- Keep your feet firmly planted to provide stability.
- If you have any lower back issues, proceed with caution, ensuring the twist does not aggravate them.
- Stop immediately if you experience pain or discomfort.
- This exercise is particularly effective for those seeking to improve their shoulder flexibility and reduce discomfort, offering a gentle way to stretch and strengthen the shoulder region.
Exercise 9: Thread the Needle
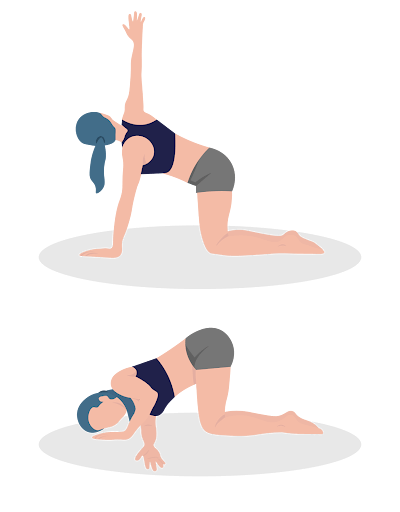
Objective: Stretch and mobilize the shoulders, chest, and upper back.
Benefits: Releases tension in the upper back and shoulders, improves flexibility.
Instructions:
- Start on all fours.
- Extend one arm under the body, palm facing up, and gently lower the shoulder to the floor.
- Hold for a moment, then unwind and switch sides.
Safety tips:
- Move into the stretch slowly and avoid putting too much weight on your shoulder or neck.
- Keep the rest of your body stable throughout the exercise.
Exercise 10: Child’s Pose
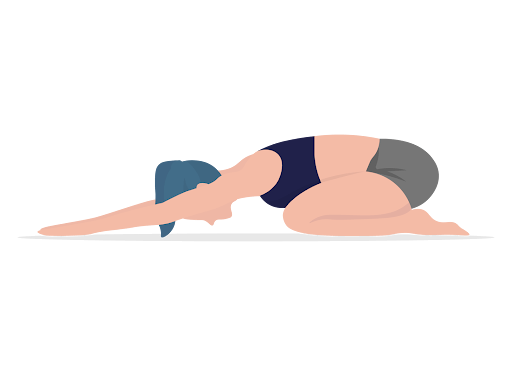
Objective: Promote relaxation and stretch the back, shoulders, and neck.
Benefits: Reduces tension in the back, shoulders, and neck; enhances flexibility.
Instructions:
- Kneel on the floor, big toes touching, and sit back on your heels.
- Bend forward, extending arms in front of you, and rest your forehead on the ground.
- Hold and breathe deeply.
Safety tips:
- Ensure comfort in your knees and hips.
- Use a cushion if needed.
- Extend your arms as far as comfortable, without straining.
Tips On Performing Shoulder Exercises
Here are some valuable tips to assist you with your shoulder exercises that will not aggravate your existing pain:
- Start slow – at least 10 minutes three times per week.
- Focus on relaxing and releasing tension.
- Stretch as far as you’re comfortable.
- Discontinue exercise if it causes more pain.
- Avoid exercises that are likely to aggravate your specific injuries.
When to See a Physical Therapist for the Pain
It’s appropriate to see a physical therapist for shoulder pain if it persists beyond a few days, limits daily activities, or is accompanied by night pain, indicating a potential underlying condition. If home remedies like rest and ice fail to relieve symptoms, or if there’s a history of shoulder problems, professional guidance can help prevent further injury. Physical therapy is also recommended for signs of swelling, deformity, or loss of joint function, to ensure proper diagnosis and treatment.
Get Expert Care for Your Shoulder Pain
Consulting with an expert is crucial in accurately diagnosing the cause of shoulder pain, which can stem from various conditions like impingement, tendinitis, or a rotator cuff injury. A combination of physical assessments and imaging tests will assist in pinpointing the exact source of pain and dysfunction.
At the Centeno-Schultz Clinic, we are experts in the evaluation and treatment of shoulder pain. It starts with an extensive review of current and past medical and surgical history, onset of pain, aggravating and alleviating factors, and a review of current imaging. An in-office ultrasound provides real-time imaging that can detect instability, tendonitis, rotator cuff tears, and arthritis.
We offer customized treatment plans that may include innovative regenerative procedures, such as platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections, aimed at healing and restoring function without the need for surgery.
This specialized approach ensures that patients receive targeted, effective treatment plans that address the underlying cause of their shoulder pain.
Managing chronic shoulder pain is possible with professional care. Consult with our experts today!