Lesions on Thoracic Spine
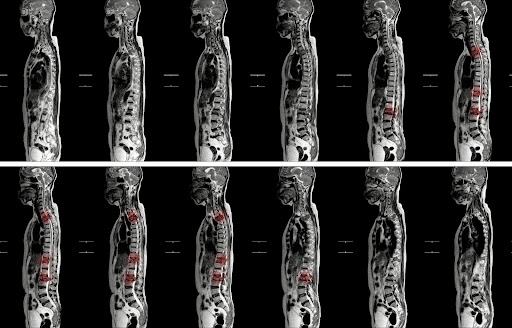
Lesions on the thoracic spine can encompass various conditions such as herniated discs, fractures, tumors, or infections. These abnormalities can lead to discomfort and functional impairments in the affected area.
In this article, we’ll discuss more about thoracic spine lesions, possible causes, and treatment options.
What Are Thoracic Spine Lesions?
A thoracic spine lesion is an abnormality in the spine itself, adjacent tissue or spinal cord. The abnormality may occur in any of the following structures:
- Vertebral Bodies: The boney building blocks that stack one upon the other to make the thoracic spine. There are 12 thoracic vertebral bodies.
- Disc: A critical shock absorber that is sandwiched between each boney building block. It is composed of a thick outer layer and soft, gelatinous center. The outer fiber is called the annulus fibrous whereas the center is the nucleus pulposus. Both structures are susceptible to injury.
- Facet Joints: Paired cartilage lined joint that restricts motion and provides stability.
- Costotransverse Joints: Cartilage lined joint created by the union of the rib and transverse process.
- Spinal Canal: Boney canal on the backside of the spine that contains and protects the spinal cord and cerebral spinal fluid (CSF).
- Neuroforamen: The boney doorway through which the exiting nerve roots travel en route to their final destination.
In the following video, I go over all of this in detail:
What Are The Thoracic Spine Lesion Symptoms?
Thoracic lesions can cause a number of different symptoms depending on their location, size, and adjacent structures. A lesion in the bone of one of the thoracic vertebral bodies will cause symptoms that are different from a lesion in the spinal cord. The most common symptoms include:
- Pain: Can be mild, moderate, or severe. Onset can be gradual or abrupt. May be on left or right side of the thoracic spine or both.
- Numbness: Compression of exiting nerves or the spinal cord can give cause numbness and tingling.
- Weakness: Compression of the motor nerve can lead to lower extremity weakness. Patients may complain of difficulty walking or balance problems.
- Movement Limitations: Lesions in the thoracic spine can limit movement due to pain and swelling.
Deep Dive
Arm Pain at Night
Arm pain at night can be miserable. The pain can interrupt your sleep and erode your quality of life. Irritability becomes increasingly more common. What are the causes? When should I worry about it? What are the treatment options for arm pain at night? The neck is composed of 7 boney building blocks numbered 1- 7. Sandwiched between the bones is a disc that functions as an important shock absorber. The cervical discs are susceptible to injury due to trauma, degeneration, repetitive motion, and surgery. Common disc injuries include disc bulges, and herniations. The injured disc can compress or irritate one or more nerves resulting in arm pain at night. It can…
Read More About Arm Pain at NightBack Pain in Ribs
Experiencing thoracic spine and rib pain? Learn more about what could be causing this and the treatment options that can provide lasting relief. Back pain in the ribs can be a common and often debilitating condition, causing discomfort and limiting mobility for many individuals. The pain can range from mild to severe and may be caused by various underlying conditions. Understanding the many causes of rib and back pain is important and can assist in securing an accurate diagnosis. Treatment options vary depending on the underlying cause and severity of symptoms.
Read More About Back Pain in RibsReferred Pain From The Thoracic Spine
Pain is the body’s way of signaling distress or injury. But what if your body manifests pain in a certain area of your body and yet the actual source of the discomfort is a completely different part of your body? In this article, we will explore the intricacies of referred pain, specifically referred pain from the thoracic spine. We’ll explore what this typically feels like, what conditions commonly cause referred pain, and the treatment options available to treat the root cause of this symptom.
Read More About Referred Pain From The Thoracic SpineThoracic Facet Joint Pain
Symptoms of a thoracic facet joint injury will vary depending upon severity of the injury and which facet joint is injured. The joints have established pain referral patterns (2). Drefus et al demonstrated that pain from a given facet joint does not occur in the immediate area of the joint in 75% of cases. Rather, it refers to an area away from the joint. For example, pain from injury of the T3/4 facet is felt along the inside border of the scapula. Unfortunately, there is significant overlap between the thoracic referral patterns which can complicate identifying the exact facet joint…
Read More About Thoracic Facet Joint PainThoracic Spine Tightness
Thoracic spine tightness can be caused by a number of different conditions. Many providers and medical practices focus on treating symptoms, with the aim of reducing them. Therefore, they provide prescriptions for different medications and referral to physical therapy with the hope that this will reduce or eliminate symptoms. At the Centeno-Schultz Clinic, we take a different approach. We believe that the first step is an accurate diagnosis. By identifying the accurate underlying issue, patients can receive the appropriate therapy and get the best clinical results. The process starts with a board-certified, fellowship-trained physician taking a detailed history that includes the onset of symptoms, presence or absence of trauma, aggravating factors, alleviating factors, and treatment to date.
Read More About Thoracic Spine TightnessUpper Back Pain Between The Shoulder Blades
Upper back pain between the shoulder blades is also known as interscapular pain. Fifteen percent of the population suffers from chronic upper back pain. Finding the source of interscapular pain can be tricky because the upper back houses many important structures like the heart, the upper lobes of the lung, the cervical spine, the scapulas, and a dozen or so of muscles and nerves.
Read More About Upper Back Pain Between The Shoulder BladesWhat Causes Thoracic Spine Lesions?
A spine lesion is an abnormality in the spine, adjacent tissue, or spinal cord. There are many different causes of thoracic spine lesions. They can be broken down into the following categories.
Trauma
Acute trauma can lead to injury and subsequent change in the tissue of the thoracic spine, adjacent tissue, or spinal cord. Common examples include motor vehicle accidents and contact sports. For example, a rear-end MVA can injure the facet joint, costotransverse joint, vertebral bodies or disc thereby creating a lesion in the thoracic spine.
Degenerative Conditions
Generalized wear and tear or post-traumatic arthritis can affect the vertebrae, discs, facet joints, costotransverse joints, spinal canal, and spinal cord leading to a thoracic spine “lesion”.
Tumors And Cysts
Benign or malignant tumors do occur in the thoracic spine. The most common malignant tumors in the spine are spinal gliomas, ependymomas, and Astrocytic tumors of the spinal cord. (1). Vertebral hemangiomas are the most common benign. Metastases from other primary cancers can also occur creating a lesion in the thoracic spine.
Inflammatory Conditions
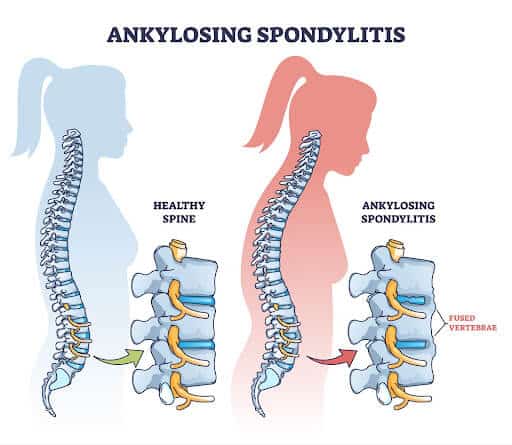
There are a number of inflammatory conditions that can cause thoracic lesions. Examples include:
- Ankylosing spondylitis: a form of arthritis.
- Arachnoiditis: an infection of the membrane that surrounds the spinal cord
- Discitis: an infection in the disc.
- Osteoarthritis: the most common type of arthritis caused by “ wear and tear” on the joints over time. It can affect the vertebral bodies, discs, facet joints, costotransverse joints, and ligaments leading to a “lesion in the thoracic spine”
Congenital Abnormalities
Common thoracic abnormalities include kyphosis, lordosis, scoliosis, and spina bifida. The two most common chest wall deformities in the thoracic spine include pectus excavatum and pectus carinatum.
Postural Issues
Poor posture, rounding of the shoulders, head forward posture, and extensive screen time can all lead to injury of the thoracic discs, facet joints, costotransverse joint, and musculature potentially leading to ‘lesion in the thoracic spine”.
Diagnostic Methods For Thoracic Spine Lesions
The evaluation of the lesion in the thoracic spine involves many steps. The first step is a detailed medical history where the following is documented: onset of symptoms, duration, location, intensity, aggravating and alleviating factors, and treatment to date.
- Physical Examination: Evaluation of range of motion, area of tenderness, motor strength, sensation to pinprick, and detailed neurologic examination.
- Radiographic Studies: Radiographic tests are essential and may include:
- X-ray: Low-cost and readily available, X-rays provide an image of the bones and can reveal fractures, dislocation, osteoporosis, and deformities like scoliosis and kyphosis. It is often the first-line diagnostic tool used to evaluate spinal conditions. Low amount of radiation exposure.
- MRI: The best option for the diagnosis of a lesion in the thoracic spine is an MRI which provides a 3d image of the bones and soft tissues that include muscle, tendons, blood vessels, nerves, discs, and thoracic joints. MRI uses a combination of magnetic fields and radio waves to create dynamic 3d images that do not use any radiation.
What Are The Common Treatments For Thoracic Spine Lesions?
Treatment depends upon the specific type of lesion and its severity. When appropriate, conservative care should be the first-line treatment. Common treatments include:
- Medications: NSAID, muscle relaxants, oral steroids, and oral narcotics.
- Physical Therapy: PT can provide a significant role in the treatment of lesions in the thoracic spine by addressing pain, improving mobility, and restoring function.
- Surgical Treatments: When conservative care and injections have failed to provide significant and sustained relief, patients may be referred for a surgical consultation. The specific surgery is dependent upon the type of thoracic spine lesion and its severity.
The Centeno-Schultz Clinic Approach
Regenerative treatment options aim to facilitate the healing and repair of damaged or injured tissue by using a patient’s own cells. This is a viable treatment alternative to both traditional pain injections and surgery in many cases. Traditional pain injections use different techniques that only address the symptoms and not the underlying injuries.
For example, traditional pain clinics use high-dose steroid injections to reduce the inflammation which has many side effects and may aggravate the underlying condition. Radiofrequency ablation cauterizes the nerve that transmits the pain signal from an injured thoracic facet joint to the brain thereby reducing the pain but not addressing the underlying facet injury.
Regenerative treatment options involve a functional spine approach (FSU) which is comprehensive in nature acknowledging that all the different parts of the spine work together in a highly synchronized fashion.
Injections are performed under X-ray or ultrasound guidance to ensure the injected cells are precisely placed into the targeted structures and not into potentially life-threatening areas such as the lungs or heart.
Bone Marrow Concentrate Containing Your Body’s Own Stem Cells
Bone marrow concentrate is extracted from the iliac crest and processed at the Centeno-Schultz Clinic to provide a customized treatment plan. Bone marrow concentrate is rich in many different cells including stem cells which can accelerate healing thereby reducing pain and increasing function.
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP)
Platelets are cells within our blood that are powerhouses of healing. They play a critical role in clot formation. They also have a large number of growth factors that can decrease inflammation and improve blood flow.
PRP injections super concentrate a patient’s platelets which can then be injected into a lesion in the thoracic spine to promote healing. PRP injections are a viable alternative to traditional pain injections. They can address and treat the underlying injury as opposed to masking the symptoms.
Embrace Optimal Spine Health
A thoracic spine lesion is an abnormality in the spine, adjacent tissue, or spinal cord. It may occur in the thoracic vertebral body, disc, facet joint, costotransverse joint, spinal canal, neuroforamen, or spinal cord.
Symptoms include pain, weakness, restriction in range of motion or numbness. Common causes of lesions of the thoracic spine include trauma, degenerative conditions, tumors, cysts, inflammatory conditions, congenital abnormalities, and postural issues.
Diagnosis includes medical history, detailed physical examination, and radiographic imaging. Treatment options depend upon the location of the lesion and its severity. When appropriate conservative treatment should always be the first line treatment of choice.
PRP and bone marrow concentrate in many cases are viable treatment alternatives to potentially addicting medications or life-changing thoracic surgery.

John Schultz, MD
John R. Schultz M.D. is a national expert and specialist in Interventional Orthopedics and the clinical use of bone marrow concentrate and PRP for orthopedic injuries. He is board certified in Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine and underwent fellowship training. Dr. Schultz has extensive experience with same day as well as culture expanded bone marrow concentrate and sees patients at the CSC Broomfield, Colorado Clinic, as well the Regenexx Clinic in Grand Cayman. Dr. Schultz emphasis is on the evaluation and treatment of thoracic and cervical disc, facet, nerve, and ligament injuries including the non-surgical treatment of Craniocervical instability (CCI).
Are you a Candidate?
More Resources for Lesions on Thoracic Spine
-
What Happens If You Have Back Pain From Golf?
Back pain is a common complaint among golfers, impacting both amateur enthusiasts and professional athletes. Golf, while seemingly low-impact, involves repetitive, high-intensity movements that can stress the spine and surrounding structures. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and preventative measures for golf-related back pain can help maintain performance and long-term health. Golf And Back Pain The golf…
-
Thoracic Spinal Fusion Recovery Explored
Thoracic spinal fusion is an intricate surgery that involves fusing vertebrae to reduce pain and improve functionality. It is often necessary due to conditions such as scoliosis, spinal fractures, or degenerative disc disease. Recovery from thoracic spinal fusion is a critical phase, requiring careful management to ensure proper healing and restoration of movement. Patients must…
-
The C1 And C2 Vertebrae – What To Know
The C1 and C2 vertebrae, also known as the atlas and axis, are the uppermost bones in the spinal column. They play a crucial role in supporting the skull and enabling head movements. Damage or injury to these vertebrae often leads to pain, limitations to daily activities, and reduced quality of life. Many patients, without…
-
Spinal Fusion Complications Years Later – What You Should Know
Spinal fusion surgery, often performed to alleviate chronic back pain or spinal instability, can lead to complications years later. These may include adjacent segment disease, where nearby vertebrae deteriorate, chronic pain, or hardware failure. Patients might also experience limited mobility and nerve damage over time. Understanding these potential risks is crucial for long-term care and…
-
Spinal Fusion Recovery: What to Expect
Navigating spinal fusion recovery can be a daunting prospect, given its impact on daily life and mobility. Understanding what to expect during this process is crucial for individuals undergoing this procedure. In this article, we’ll explore the typical timeline, challenges, and strategies for managing recovery after spinal fusion surgery, providing insights to help individuals prepare…
-
Back Cracking: The Truth of What’s Actually Happening in Your Body
Back cracking is a phenomenon that many people experience, often eliciting both curiosity and concern. Whether it’s the satisfying pop from a morning stretch or the deliberate twist during a yoga session, the sound and sensation of cracking your back can be oddly gratifying. But what exactly is happening inside your body when you hear…
References
- Kumar N, Tan WLB, Wei W, Vellayappan BA. An overview of the tumors affecting the spine-inside to out. Neurooncol Pract. 2020 Nov 18;7(Suppl 1):i10-i17. doi: 10.1093/nop/npaa049. PMID: 33299569; PMCID: PMC7705529.