Thoracic Spondylosis
Spondylosis is a medical term that refers to a degenerative condition affecting the spine. It is a common condition that occurs because of wear and tear in the spine, typically due to aging or injury. Spondylosis can affect any part of the spine.
What is Thoracic Spondylosis?
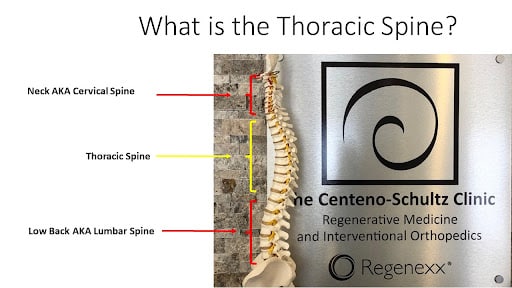
The thoracic spine, also known as the mid back, is that portion of the spine that is below the cervical spine (neck) and above the lumbar spine (low back). Thoracic spondylosis is a degenerative condition of the thoracic spine.
The thoracic spine, also known as the mid back, is composed of many important different structures that work together to provide stability and movement.
The major components include:
- Vertebrae: 12 boney building blocks that stack one upon another.
- Thoracic Disc: 12 fibrocartilaginous cushions sandwiched between the vertebrae that act as shock absorbers.
- Thoracic Joints: 3 important joints: thoracic facets, thoracic costotransverse and costovertebral
- Thoracic Muscles: three principal layers: superficial, intermediate and deep muscles.
- Thoracic Ligaments: multiple dense bands of connective tissue that hold bones together. Think of them as duct tape for the body.
- Thoracic Nerves: Multiple nerves that are responsible for sending and receiving signals from the muscles, skin, and organs in the chest and upper abdomen.
Causes And Risk Factors Of Thoracic Spondylosis
Thoracic spondylosis is a degenerative condition affecting the middle region of the spine, known as the thoracic spine. The major causes include:
Aging
With age, there is a generalized wear and tear on the thoracic spine. The discs lose their water content and become less flexible. They also tend to become smaller in size which can lead to the development of bone spurs, nerve root irritation, facet joint arthritis, and ligament laxity (1).
Genetics
Some people may be more prone to developing thoracic spondylosis due to genetic factors.
Poor Posture
Poor posture for extended periods can cause excessive stress on the thoracic vertebrae, discs, facet joints, and ligaments and can lead to the development of thoracic spondylosis.
Repetitive Strain
Activities that involve repetitive movement or heavy lifting can cause wear and tear on the spine, leading to spondylosis.
Trauma
Trauma to the spine, such as a fall or car accident, can cause damage to the thoracic disc, facet joints, and ligaments and this can lead to spondylosis (2).
Symptoms Of Spondylosis Of The Thoracic
Thoracic spondylosis is a degenerative condition that affects the thoracic spine. Symptoms can be mild, moderate, or severe depending upon the location and severity of degenerative changes. The most common symptoms associated with thoracic spondylosis include:
Back Pain
One of the major symptoms of spondylosis of the thoracic spine is mid back pain. The pain can be intermittent or constant. It can be isolated to one side or may involve both sides of the spine.
The severity of the pain is dependent upon many factors that include the location and severity of the degenerative changes. The back pain can be dull and throbbing or electrical and stabbing. It may be localized along the spine or can radiate across the chest wall or into the abdomen.
Stiffness
Stiffness is common in patients with thoracic spondylosis as the disc’s lose their water content and ability to act as shock absorbers. The forces of daily living are then transferred to the vertebrae bodies, posterior facet joints, and supporting ligaments. The resulting pressure and inflammation can cause symptoms like pain, stiffness, and restricted range of motion.
Tingling or numbness
Tingling and numbness are common symptoms associated with thoracic spondylosis. The thoracic discs can become injured with a loss in disc height or disc protrusions. Disc injuries in turn can cause compression of the nerves in the thoracic spine, leading to a sensation of tingling and numbness in the affected area.
As the condition progresses, the numbness may spread to other parts of the body, such as the arms, legs, and hands. In severe cases, thoracic spondylosis can also lead to muscle weakness, loss of balance, and difficulty walking.
Back Pain in Ribs
Experiencing thoracic spine and rib pain? Learn more about what could be causing this and the treatment options that can provide lasting relief. Back pain in the ribs can be a common and often debilitating condition, causing discomfort and limiting mobility for many individuals. The pain can range from mild to severe and may be caused by various underlying conditions. Understanding the many causes of rib and back pain is important and can assist in securing an accurate diagnosis. Treatment options vary depending on the underlying cause and severity of symptoms.
Read More About Back Pain in RibsBig Toe Numbness
Believe it or not, one of those significant issues that can present as numbness stems from the low back. In the lumbar spine, the nerve that exits the spine at the L5 level branches down through the hip, thigh, knee, lower leg, and, yes, all the way into the foot and toes. So a pinched or irritated nerve at that L5 level in the back can create problems, such as pain, numbness, tingling, and so on, anywhere along the nerve branch. So what can irritate the L5 spinal nerve? The list is long, but it includes disc issues, such as herniated…
Read More About Big Toe NumbnessLeg Feels Disconnected
So what exactly causes the leg to feel disconnected? The hip joint is the connection point between the leg and the rest of the body. The femur in the leg and the acetabulum in the pelvis create the hip joint. So if the left SI joint, for example, in the back and the symphysis pubis joint in the front becomes unstable due to loose supporting ligaments, then the left leg, which is connected between the two joints, is likely to also feel a bit disconnected. Likewise, if the right SI joint were unstable, then the right leg might feel disconnected. How This Patient’s “Disconnected” Leg Was Fixed Despite “leg feels…
Read More About Leg Feels DisconnectedLeg Gives Out
Have you ever been walking and your leg gives out? It can be both surprising and alarming What would cause your leg to give out? Can sciatica cause your leg to give out? How do you treat weak legs? Let’s dig in.Weakness in the leg can arise from three principal sources: nerve problems, muscle weakness, and SI joint dysfunction. Weakness in the legs may indicate a significant nerve problem. In many cases, it may be the first indication of a nerve problem. There are three common causes of nerve injury: low back disorders, nerve compression as it descends down into the hip, thigh, and shin and medical conditions such as diabetes…
Read More About Leg Gives OutLower Back Pain When Sitting
After a long day on your feet sitting down is supposed to be way to relaxing. Unfortunately for some sitting for any length of time can be painful. Most people experience low back pain at some point in their life. The lifetime prevalence of low back pain is 85% (1). Let’s take a deeper look at the different types of pain and causes of low back pain when sitting. Pain can present in many different ways. It can be intermitent or constant. The quality of the low back pain can also vary depending upon the actual source of injury. Common examples include: Sharp and Stabbing, Dull and Aching, Throbbing/ Pulsating, Pins and Needles, Burning, Electrical
Read More About Lower Back Pain When SittingLower Back Pain When Standing
When you’re seated, the facet joints in your lower back are in an open and slightly flexed position. When you stand up, these joints compress. If they are painful or have arthritis, you’ll have pain as you stand up because this puts pressure on the painful joints. In addition, if there is any type of movement of one vertebra forward on another (called spondylolisthesis), then this shift will have occurred as you sit. This is called degenerative spondylolisthesis. When you get back up, the vertebrae will come back into position after a few seconds, leading to that awkward “walk it out period” that starts out painful and ends up more normal.
Read More About Lower Back Pain When StandingNerve Pain in the Thoracic Spine
The thoracic spine is the part of the spine below the neck (cervical spine) and above the low back (lumbar spine). It is often referred to as the mid back. Nerves exit the thoracic spine at each level and can become irritated, compressed or injured, resulting in pain and dysfunction. This is commonly referred to as thoracic radiculopathy or pinched nerve.
Read More About Nerve Pain in the Thoracic SpineReferred Pain From The Thoracic Spine
Pain is the body’s way of signaling distress or injury. But what if your body manifests pain in a certain area of your body and yet the actual source of the discomfort is a completely different part of your body? In this article, we will explore the intricacies of referred pain, specifically referred pain from the thoracic spine. We’ll explore what this typically feels like, what conditions commonly cause referred pain, and the treatment options available to treat the root cause of this symptom.
Read More About Referred Pain From The Thoracic SpineDiagnosis Of Thoracic Spondylosis
The diagnosis of thoracic spondylosis usually involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and radiographic imaging tests.
Important questions during the medical history include onset of symptoms, triggering events, location of pain, numbness and tingling, aggravating factors and alleviating factors. Other important questions include past medical and surgical history and current medications.
During physical examination the doctor will evaluate a patient’s range of motion, muscle strength, reflexes, and sensation to light touch and pin prick.
Imaging tests are most often used to confirm the diagnosis for thoracic spondylosis. Thoracic x-rays are beneficial as they are widely available, low cost, with little radiation exposure. X-rays provide detailed images of the bony structures of the spine and can identify bone spurs, fractures, and injury to the disc.
Unfortunately, they do not provide detailed information on the discs, facet joint, ligaments, tendons, nerves, or the spinal cord.
MRI is the gold standard in the diagnosis of thoracic spondylosis (3). MRI uses a powerful magnetic field and radio waves to produce detailed images of the body. Thoracic MRI clearly details the spinal cord, spinal nerves, discs, ligaments, and tendons and can detect both large and small abnormalities.
Common Treatment Options
Thoracic spondylosis is a degenerative condition that affects the thoracic spine. It can cause pain, stiffness, restricted range of motion, and numbness and tingling in the extremities. Treatment options include conservative therapy, medications, injections and in severe cases possibly surgery. When appropriate, the first line of treatment should be conservative care.
The best treatment option depends on many factors which include the severity of the spondylosis, a patient’s symptoms, past medical condition, current medications and access to treatment. The most common treatment options include:
NSAIDs
The other day I was evaluating a patient and reviewing the treatment options for their spine condition. After discussing prior treatments, we got to the topic of medications taken for pain relief. She explained that she mainly utilized anti-inflammatory (NSAID) medications and then she told me to hold much she takes and has been for many years…..she takes close to 2 grams (2000 milligrams) on a daily basis which equated to about 9-10 capsules of medication per day. I was shocked, considering she was pre-diabetic and with high blood pressure plus the kicker of it is that her PCP (primary care physician) is ok with this…
Read More About NSAIDsThoracic Spine Surgery
Thoracic spine surgery is a major surgery aimed at treating injuries in the thoracic spine. Because of the complex anatomy and close proximity to the heart and lungs, there are significant surgical risks and complications. Surgery on the thoracic spine can take hours and may require deflating the lung in order to gain access to the thoracic injury. Recovery can be lengthy depending upon the specific thoracic spine surgery performed. There are several different types of thoracic spine surgery. The specific thoracic spine performed depends upon the underlying thoracic injury and a symptoms of the patient. For example, a thoracic disc herniation…
Read More About Thoracic Spine SurgerySurgery
Patients that fail to get significant or sustained benefit from conservative care, medications, and steroid injections are often referred for surgical consultation. Surgery should be the last option given the significant complications and complex anatomy. The exception are those patients with progressive neurologic deficits such as weakness, numbness, or tingling in the arms or legs.
Surgery may also be considered in cases of spinal instability that are threatening an individual’s quality of life. The most common surgeries include thoracic laminectomy, thoracic discectomy, and fusion. All are major surgeries with significant and potentially permanent complications which have been discussed in a previous blog.
Regenerative Options For Thoracic Spondylosis
At the Centeno-Schultz Clinic, regenerative treatment options are available for the treatment of thoracic spine injuries including thoracic spondylosis. Regenerative treatment options utilize the healing potential of your body’s own cells.
Treatment options include bone marrow concentrate, prolotherapy and PRP. All injections are customized and performed under ultrasound or x-ray guidance. Regenerative treatment options allow patients to forgo the toxicity of steroids, the potential dependence of medications, and complications of surgery.
Bone Marrow Aspirate Concentrate
Bone marrow aspirate also known as Regenexx SD is a procedure in which bone marrow is harvested from a patient, processed in the state of art cell laboratory, and injected in the area of tissue damage. Bone marrow concentrate contains stem cells.
These repair cells live inside all of us and are poised to leap into action to repair damage as it occurs. The bone marrow concentrate is customized for each patient in the lab as opposed to using the “one size fits all” approach commonly used by many stem cell clinics.
Prolotherapy Injections
It has been successful in the treatment of many disorders including neck, shoulder, knee, and ankle pain. Dr. Centeno recently published an article in The Journal of Prolotherapy in which he discusses the use of x-ray guidance with prolotherapy. This ensures that the injection is in the correct place to maximize clinical results. Dr. Centeno discusses the use of prolotherapy for the treatment of neck, knee, sacroiliac joint, ankle, ischial tuberosity, and shoulder pain. At the Centeno-Schultz Clinic x-ray guided prolotherapy is just one of the therapies utilized in the successful treatment of pain. Regenerative injection therapy (RIT) or prolotherapy…
Read More About Prolotherapy InjectionsPRP Injections
PRP is short for platelet-rich plasma, and it is autologous blood with concentrations of platelets above baseline values. The potential benefit of platelet-rich plasma has received considerable interest due to the appeal of a simple, safe, and minimally invasive method of applying growth factors. PRP treatments are a form of regenerative medicine that utilizes the blood healing factors to help the body repair itself by means of injecting PRP into the damaged tissue. In regenerative orthopedics, it is typically used for the treatment of muscle strains, tears, ligament and tendon tears, minor arthritis, and joint instability. There have been more than 30 randomized controlled trials of PRP…
Read More About PRP InjectionsProlotherapy For Thoracic Pain
Prolotherapy is an injection based regenerative therapy used in the treatment of ligament, tendon, muscle and spine injuries. It is minimally invasive and involves the injection of an irritant such as dextrose into the damaged or painful area. The injected irritant stimulates a delayed or frozen healing cycle thereby increasing blood flow and tissue healing. The thoracic spine is that section of the spine that is below the neck and above the low back. It is also referred to as the mid back. It has multiple components that include: Vertebral Bodies: Boney building blocks that stack one upon another…
Read More About Prolotherapy For Thoracic PainExperience The Centeno-Schultz Difference
Thoracic spondylosis is a degenerative condition of the thoracic spine. It can affect the thoracic vertebrae, discs, thoracic joints, muscles, ligaments, nerves, and spinal cord.
Major causes include aging, genetics, poor posture, repetitive sprain, and trauma. Symptoms include pain, stiffness, restriction in range of motion, tingling, and numbness.
Diagnosis involves medical history, physical examination, and radiographic imaging tests. MRI is the gold standard as it allows for clear visualization of the discs, facet joints, ligaments, tendons, spinal cord, and nerves.
Conservative care when appropriate should always be first line treatment. Other options include medications and steroid injections. Thoracic spine surgery is major surgery and associated with significant risks. It may be indicated in patients with progressive neurologic symptoms or instability.
Regenerative treatments include bone marrow concentrate, prolotherapy, and PRP which allows patients to use their own healing cells and avoid the risks of steroids, medications, and potentially surgery.
At the Centeno-Schultz Clinic we are experts in the evaluation and treatment of thoracic spine injuries. Board certified, fellowship trained physicians can evaluate your candidacy for regenerative, non-surgical treatment options.
Thoracic pain is poorly understood and oftentimes mismanaged. Come to the experts and learn which regenerative treatments are best for you or a loved one.

John Schultz, MD
John R. Schultz M.D. is a national expert and specialist in Interventional Orthopedics and the clinical use of bone marrow concentrate and PRP for orthopedic injuries. He is board certified in Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine and underwent fellowship training. Dr. Schultz has extensive experience with same day as well as culture expanded bone marrow concentrate and sees patients at the CSC Broomfield, Colorado Clinic, as well the Regenexx Clinic in Grand Cayman. Dr. Schultz emphasis is on the evaluation and treatment of thoracic and cervical disc, facet, nerve, and ligament injuries including the non-surgical treatment of Craniocervical instability (CCI).
Not sure what treatment path to follow? Consult us to get expert opinion on diagnosing your condition!
More Resources
-
Understanding the Thoracic and Lumbar Spines
The thoracic spine and lumbar spine make up a vital nexus of stability and mobility in the human body. In this exploration, we delve into the biomechanics and complexities that define these regions, unraveling their significance in posture, movement, and overall well-being. Understanding the thoracic and lumbar spine not only illustrates the mechanics of our…
-
Understanding the Role Of The Thoracic Spine Muscles
The thoracic spine plays a critical role in the stability and mobility of the upper body. Comprised of twelve vertebrae and an intricate network of muscles and ligaments, it serves as a central pillar supporting the structure and movement of the body. Understanding the role and function of thoracic spine muscles is pivotal for anyone…
-
Degenerative Changes Of The Thoracic Spine
Degenerative changes of the thoracic spine involve the gradual loss of normal structure and function over time. There are several different causes which are discussed in detail below. The thoracic spine is composed of many different and important components that are susceptible, both to injury and generalized wear and tear. The degeneration can occur in…
-
The Ultimate Guide To Thoracic Spine Exercises
Thoracic spine exercises are important for several reasons. First, they can help improve thoracic mobility, reducing the risk of spinal injuries and improving posture. Second, they can help to strengthen the muscles of the upper back and shoulders. Finally, thoracic spine exercises can help improve breathing mechanics. What Is Thoracic Spine? The thoracic spine, also…
-
Where Is The Thoracic Spine?
The thoracic spine is a region of the spine that is located in the middle back. It is located below the cervical spine and above the lumbar spine. It is composed of 12 vertebrae that are numbered T1-12. The T denotes the thoracic spine. It has many important functions which are discussed below. Location Of The…
-
Symptoms of Thoracic Herniated Disc
Your mid back pain has been unrelenting since the accident. Rest, medications, and physical therapy have failed to provide significant or sustained benefits. Your doctor thinks you have a thoracic disc herniation and thinks you have a thoracic herniated disc. What are the symptoms? And what can you do? Let’s dig in. What Is A…
References
1.Lauerman, W. C., & Stetkarova, I. (2018). Age-related changes in the spine: a review of spinal pathology through the human life span. The American Journal of Orthopedics, 47(12).
2.Furlan, J. C., Catharine Craven, B., Fehlings, M. G., & Shannon, P. (2006). Spondylotic myelopathy: a clinical and radiological evaluation of the consequences of traumatic injury. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry, 77(7), 944-947.
3.Ahn SH, Ahn MW, Byun WM. Effectiveness of magnetic resonance imaging in diagnosing thoracic myelopathy caused by thoracic spondylosis. Int Orthop. 2003;27(3):152-154. doi:10.1007/s00264-002-0402-9