The rotator cuff is compromised for four principle muscles: the supraspinatous, teres minor, subscapularis, and infraspinatus. A rotator cuff tear is usually the result of a sudden powerful raising of the arm against resistance. Common examples include heavy weightlifting or falling on an outstretched arm. Acute tears are associated with severe pain often shooting down the arm, limited range of motion, and point tenderness at the site injury.
The supraspinatus originates from the scapula (shoulder blade) and attaches via a tendon to the humerus. It functions to stabilize the shoulder joint and enables one to raise their arm in the plane similar to a jumping jack.
Supraspinatus rotator cuff tears are often treated with surgery where the tendon is reinforced and stapled onto the humerus. The surgery requires rotator cuff rehabilitation which can be painful and extensive.
Stem cell therapy is now an alternative therapy for partial tears of the rotator cuff. At Regenexx patients are able to use their own stem cells to repair partial tears in tendons and ligaments. Regenexx is a simple needle-in, needle-out procedure which enables patients to forgo surgery and the extensive rehabilitative process typically associated with rotator cuff surgery.
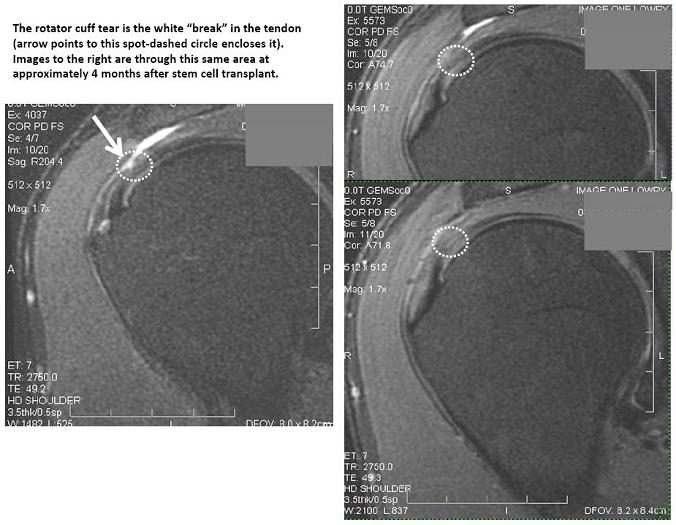
Please see images below where a patient used their own stem cells to repair a partial supraspinatus tear.