The searing back pain came out of nowhere. You crumple over in agony, unable to move. Your doctor thinks you may have injured your disc.
What is a herniated disc? How is a herniated disc diagnosed? Can a herniated disc heal on its own? What are the treatment options for a herniated disc? How can a herniated disc heal naturally?
Let’s dig in.
What Are Spine Discs?
The spine is composed of bony building blocks called vertebral bodies. They are numbered and their specific location is noted by one of three letters: C, T, or L, indicating cervical, thoracic, or lumbar.
Sandwiched between the vertebral bodies are shock absorbers called discs. A disc has two principal parts: the jelly-like inside called the nucleus pulposus and the tough outer layer called the annulus fibrosus (1).
How Does a Herniated Disc Happen?
A disc herniation is when the jelly-like inside of the disc ruptures through the tough outer wall (2). Think of it like a pimple that has popped.
The ruptured material is highly inflammatory and can:
- Cause severe irritation and swelling in the area of the herniated disc (localized pain)
- Place pressure on a spinal nerve, causing pain to radiate down the arm or leg (radicular)
A disc herniation is NOT a disc bulge or protrusion as, in both those conditions, the jelly-like material is still contained in the disc. Disc herniation occurs most commonly in the lumbar spine between the fourth and fifth decade of life (3).
Factors associated with lumbar disc herniation include genetic predisposition (4), disc degeneration (5), and excessive loading (6).
Lumbar disc herniation is the condition that most often leads to spinal surgery, especially among men around the age of 40 years (7).
Who Is at Risk?
A herniated disc, also known as a slipped or ruptured disc, can affect anyone, but certain factors may increase the risk of developing this condition. Some common risk factors include:
- Age: The risk of herniated discs increases with age. Discs tend to lose water content and flexibility over time, making them more prone to herniation.
- Occupation: Jobs that involve repetitive lifting, pulling, pushing, or twisting movements, as well as those that require prolonged sitting, can contribute to the development of herniated discs.
- Genetics: There may be a genetic predisposition to developing disc problems. If close family members have a history of herniated discs, there may be an increased risk.
- Weight: Excess body weight can put additional stress on the spine and increase the risk of disc herniation.
- Smoking: Smoking has been associated with an increased risk of disc degeneration, which can contribute to herniated discs.
- Inactivity: Lack of regular exercise and physical activity can weaken the muscles that support the spine, making it more susceptible to disc herniation.
- Improper lifting: Lifting heavy objects with improper techniques, such as bending at the waist instead of the knees, can increase the risk of disc herniation.
- Gender: Men are more likely than women to develop herniated discs, although the reason for this difference is not entirely clear.
- Trauma: Injuries or trauma to the spine, such as a fall or car accident, can increase the risk of disc herniation.
Ways to Avoid Having a Herniated Disc
While it’s not always possible to prevent a herniated disc, certain lifestyle choices and habits can help reduce the risk of developing this condition. Here are some ways to minimize the likelihood of a herniated disc:
- Maintain a healthy weight: Excess body weight can put additional strain on the spine. Maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise can help reduce the risk of disc problems.
- Practice proper lifting techniques: When lifting objects, use your legs rather than your back. Bend at the hips and knees, keep the object close to your body, and avoid twisting while lifting. Keep your spine in a neutral position.
- Strengthen core muscles: Engage in exercises that strengthen the muscles supporting the spine, particularly the deep core muscles (transverse abdominals, multifidus) and glut strengthening. A strong core provides better support and stability for the spine.
- Stay active: Regular exercise helps keep the spine flexible and strengthens the muscles that support it. Include activities like walking, swimming, or low-impact aerobics in your routine.
- Maintain good posture: Be mindful of your posture, whether sitting or standing. Avoid slouching and use ergonomic furniture when possible. If you have a desk job, make sure your workstation is set up to promote good posture.
- Quit smoking: Smoking is associated with an increased risk of disc degeneration. Quitting smoking can have numerous health benefits, including a positive impact on spinal health.
- Stay hydrated: Proper hydration is essential for maintaining the health of the spinal discs. Water helps keep the discs hydrated and supports their ability to absorb shock.
- Take breaks during prolonged sitting: If you have a sedentary job or spend long periods sitting, take regular breaks to stand, stretch, and move around. This helps prevent stiffness and reduces the pressure on the spinal discs.
- Walk more: The motion of walking helps to get nutrients to the disks.
- Use proper ergonomics: Whether at work or home, make sure your environment is ergonomically friendly. Use chairs, desks, and other equipment that support good posture and minimize strain on the spine.
- Practice safe exercise techniques: If you engage in physical activities such as weightlifting or sports, make sure to use proper techniques and warm up adequately before exercising to avoid unnecessary stress on the spine.
Can a Herniated Disc Heal on its Own?
Despite what a surgeon may advise you – the answer is YES. Lumbar discs healing on their own is well documented using MRI (9). The medical term for this is a regression, which references a resolution or reduction of the disc herniation.
The healing may be partial or complete. The largest obstacle to healing spinal injuries is the poor blood supply. Blood flow is critical to healing as it brings important nutrients and healing proteins to the area of injury.
How and why regression occurs is not fully understood. The three most popular theories:
- The herniated disc becomes dehydrated and shrinks in size (10).
- Tension from the adjacent ligament (PLL) forces the herniated disc back into place (9).
- The herniated disc is absorbed by the body (11).
How to Diagnose a Herniated Disc
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is the gold standard for imaging (8). As X-rays only demonstrate the bone, they cannot identify disc herniation and cannot visualize any soft tissue such as discs, tendons, or ligaments. If your spine pain is constant and radiating down your arm or leg, insist upon an MRI.
What Are the Common Treatment Options for a Herniated Disc?
The specific treatment for a herniated disc will depend upon the extent of the disc herniation, its location, whether it is compressing a nerve, and the presence or absence of muscle weakness or numbness in the arm or leg.
When appropriate, physical therapy is the first-line treatment. The focus is on mobilization, neutral spinal alignment, and core stabilization. Some exercises such as McKenzie type can help your body absorb the herniation as well.
Supplements
Inflammation can cause significant problems and delay recovery. A recent study looked at 100 patients with low back disc herniations and followed them for one year (12). Those with elevated inflammation markers (IL-6) were approximately 3.5x less likely to recover that year.
Good quality fish oil and turmeric are safe and effective anti-inflammatory agents. NSAID medications like Motrin, Aleve, and Celebrex are toxic to stem cells and associated with a higher risk of sudden death by heart attack. NSAIDs therefore should be only used sparingly. Oral steroids are even more toxic than NSAIDs and should be completely avoided.
Surgery
When conservative therapy fails, surgery is often recommended. There are several different types of back surgery for disc herniations. All accomplish the same thing, which is cutting out the herniated disc. This procedure is called a discectomy.
Different surgical approaches differ in invasiveness. Open discectomy cuts through the lower back muscles and has many different problems including killing off important spinal stabilizing muscles.
The newer approaches are minimally invasive and utilize small cameras and instruments. The procedures work the same as far as outcomes and complications, but the minimally invasive procedure has a quicker recovery time (13).
Unfortunately for patients, the failure rate of spinal surgery ranges from 10-50% (14-16). This means the patients were classified as having continued low back or leg pain or new disabling symptoms after the surgery, which is called failed back surgery syndrome. To learn how to avoid failed back surgery syndrome please see my previous blog.
Given the issues with back surgery for disc herniations, the important question becomes how to heal a herniated disc naturally.
Is There a Natural Way to Treat a Herniated Disc?
In answer to your question about there being a way to heal a herniated disc naturally, yes!
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) is an effective treatment option for herniated discs. PRP is rich in growth factors that increase blood flow and reduce inflammation. Recall that most structures in the spine have little or poor blood flow. This poor blood flow, in turn, makes healing and repair difficult.
PRP injections can overcome this issue as the growth factors can increase the blood flow to the herniated disc. A specialized PRP product, called platelet lysate, can be injected around the irritated nerves and herniated disk to naturally reduce inflammation and promote healing. If spinal facet joints or spinal ligaments are damaged, they also can be helped by PRP injections. To learn more about PRP please click on the video below.
Meet JR, a patient at the Centeno-Schultz Clinic who had severe low back pain due to low back disc herniation in 2017. He declined surgery and opted to treat his herniated disc naturally and underwent PRP epidural and facet injections. His pain quickly improved, and JR returned to all his normal activities within several weeks after the injections.
Below are his low back MRI images before and after PRP injections.
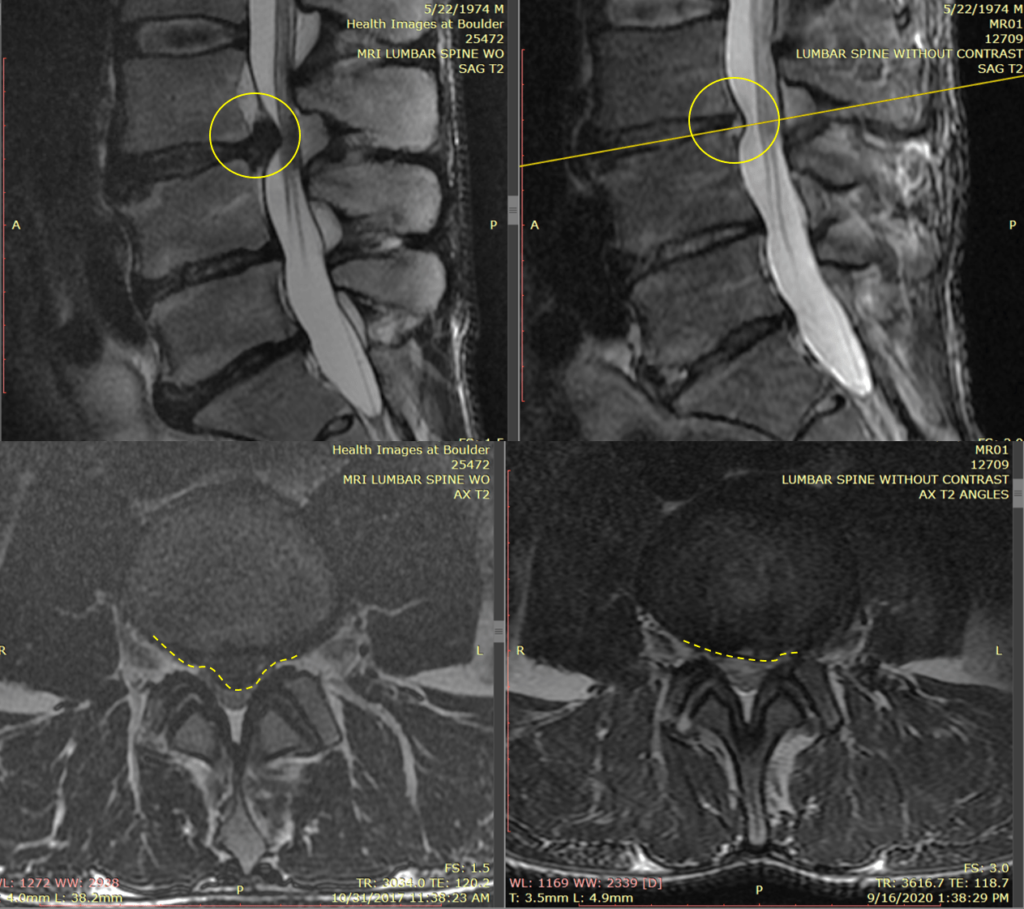
The MRI images on the left are before the PRP injection. The top left image is looking at the patient’s side. The bottom left is called an axial image and is the image if we saw JR in half. The disc herniation is the dark protruding object circled in yellow. In the top image, the yellow circle is solid, whereas in the lower image, it is dashed.
OUCH! It is no wonder that JR had severe low back pain. The images on the right are two years after the PRP injections and the resolution of pain. The yellow circle in the top right image and the dashed circle in the bottom right image show a significant reduction in size in the disc herniation. This corresponds with the 100% resolution of pain.
If you are interested in learning more about how to read and understand your low back MRI report, please click on the video below.
What to Expect after PRP Injections
If you undergo PRP injections for a herniated disc, here are some general expectations, but it’s crucial to discuss specific details and potential outcomes with your healthcare provider:
- Pain relief: Most individuals will experience pain relief or a reduction in symptoms following PRP injections which is a primary goal. The growth factors present in the platelets are believed to promote tissue healing and reduce inflammation.
- Gradual improvement: Improvement may occur gradually over time rather than immediately after the injections. It may take several weeks or months for the full effects to be noticeable.
- Limited side effects: PRP injections are generally considered safe because they use the patient’s own blood, reducing the risk of adverse reactions. However, as with any medical procedure, there may be minimal side effects such as temporary soreness or swelling at the injection site.
- Activity modification: Your healthcare provider may recommend modifications to your activities or exercises to support the healing process. It’s important to follow their advice for optimal results.
- Physical therapy: In conjunction with PRP injections, your healthcare provider may recommend physical therapy to strengthen the muscles surrounding the spine and improve overall spinal health.
- Follow-up assessments: Your healthcare provider will likely schedule follow-up appointments to assess your progress and determine whether additional treatments or adjustments are necessary.
- Variable outcomes: The effectiveness of PRP injections can vary from person to person. While most individuals may experience significant improvement, others may not respond as favorably. Patient factors that may contribute to less success can be things such as genetics, overall health, weight, smoking, diligence with physical therapy, etc. On the provider side, all PRP is not the same. High quality PRP is typically higher dose and highly concentrated from a larger blood draw. Only a handful of providers can make platelet lysate also. Precise placement of the PRP under Xray or ultrasound guidance is essential, and an accurate diagnosis key as well.
Are There Activities to Avoid?
If you have a herniated disc, certain activities may exacerbate your symptoms or put additional strain on your spine. While each person’s condition is unique, and recommendations may vary based on the severity and location of the herniation, here are some general activities that individuals with a herniated disc may need to avoid:
- Heavy lifting: Avoid lifting heavy objects, as this can put excessive pressure on the spine. If lifting is necessary, use proper lifting techniques, such as bending at the knees and keeping the object close to your body.
- Twisting movements: Minimize activities that involve twisting or rotating the spine, especially when lifting or carrying objects. Sudden or repetitive twisting motions can increase the risk of further injury.
- High-impact activities: Activities that involve repetitive impact on the spine, such as running or jumping, may worsen symptoms. Consider low-impact exercises like walking or swimming instead.
- Sitting for prolonged periods: Prolonged sitting can increase pressure on the discs, especially in a slouched or hunched position. Take breaks, stand, and stretch periodically if you have a sedentary job or lifestyle.
- Poor posture: Maintain good posture to avoid putting unnecessary stress on your spine. This includes sitting and standing with a straight back, avoiding slouching, and using ergonomic furniture when possible.
- Coughing or sneezing: While these are natural bodily functions, they can sometimes exacerbate pain associated with a herniated disc. If possible, support your spine and minimize sudden movements during coughing or sneezing. If possible, try to sneeze or cough looking upward instead of bending over.
- Bending at the waist: Instead of bending at the waist to pick up objects, bend at the knees and hips. This helps distribute the load more evenly and reduces stress on the lower back.
- Excessive flexion or extension: Avoid excessive forward bending (flexion) or backward arching (extension) of the spine. These movements can aggravate a herniated disc, so be mindful of your body mechanics.
- High-impact sports: Engaging in high-impact sports like football or basketball may not be advisable, as they involve sudden, jarring movements that can strain the spine.
- Poor body mechanics: Be mindful of your body mechanics in various activities. Whether you’re lifting, sitting, or exercising, using proper form and technique can help prevent further strain on your spine.
How to Recover Quickly from PRP Injections
Recovery from PRP injections can vary from person to person, and the speed of recovery depends on factors such as the specific condition being treated, the individual’s overall health, and adherence to post-injection guidelines. While there is no guaranteed way to speed up the recovery process, here are some general tips that may help enhance the healing and recovery after PRP injections:
- Follow the healthcare provider’s instructions: Adhere to any post-injection guidelines provided by your healthcare provider. This may include specific instructions on activity modification, rest, and any prescribed medications.
- Rest and limit activity: Allow your body time to heal by avoiding strenuous activities, heavy lifting, and high-impact exercises in the initial days following the PRP injections. Your healthcare provider may provide specific recommendations based on your condition. Rest s=does not mean bed rest however, as that can slow recovery. Easy movements and short walks can aid in getting nutrients to the disks.
- Use an infrared heating pad: Infrared heating pads can help with pain relief and increase blood flow to the affected area aiding in the healing response. Ice is not typically recommended as it can reduce blood flow and healing, though it may provide temporary pain relief. Follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations regarding the use of the heating pad as you do not want to overdo the heat also.
- Stay hydrated: Adequate hydration supports overall healing and can contribute to the effectiveness of PRP therapy. Drink plenty of water unless your healthcare provider advises otherwise.
- Avoid anti-inflammatory medications: In most cases, your healthcare provider will recommend avoiding anti-inflammatory medications (such as NSAIDs) for at least 2 weeks after PRP injections, as they could interfere with the natural healing process. Always follow your provider’s advice regarding medication use.
- Gradual return to activity: Once your healthcare provider gives the green light, gradually reintroduce normal activities and exercises. Start with gentle movements and low-impact exercises before progressing to more strenuous activities.
- Physical therapy: Your healthcare provider should recommend physical therapy as part of your recovery plan. Physical therapists can provide exercises and stretches to help strengthen the treated area and improve overall mobility.
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle: Adopting a healthy lifestyle can contribute to the overall success of PRP therapy. This includes eating a balanced diet, getting adequate sleep, and avoiding habits that may hinder the healing process, such as smoking.
- Communicate with your healthcare provider: If you experience any unexpected or worsening symptoms during your recovery, communicate promptly with your healthcare provider. They can assess your condition and make any necessary adjustments to your treatment plan.
- Be patient: Healing takes time, and the effects of PRP therapy may not be immediately apparent. Be patient and allow your body the necessary time to respond to the treatment.
Take Your Life Back from Orthopedic Pain without Surgery
A disc herniation is when the jelly-like center of the disc ruptures through the tough outer sidewall. Herniations occur most frequently in the low back. They can cause severe localized low back pain or radiating nerve pain down the leg or both.
PRP is an effective non-surgical treatment option for disc herniation. PRP is a way to heal disc herniations naturally without the risk and complications of spinal surgery.
If you have sustained a disc herniation, know that you have treatment options. Surgeons are biased towards surgery, but the operating room is not the only solution.
Schedule a telemedicine consult and learn from a board-certified physician about your treatment options.
There’s always a non-surgical solution for your back pain. Make an appointment with us today!

