Denver Neuropathy Treatment
Am I a Candidate?Platelet-Rich Plasma Injections for Peripheral Neuropathy
Peripheral nerves are essential for coordinating movement and maintaining overall body function. Unfortunately, these nerves are susceptible to damage, which can lead to a range of symptoms and interfere with everyday activities. Supporting the repair and restoration of these nerves is one of our specialties.
Our team has developed a non-surgical, less invasive procedure that uses image-guided injections. This innovative technique utilizes autologous biologics—growth factors from the patient’s own body—to promote nerve health and recovery, potentially reducing the need for more invasive surgical interventions.
How Does It Work?
Peripheral neuropathy (PN) occurs when peripheral nerves are damaged. These nerves transmit signals between the brain, spinal cord, and other parts of the body. Damage to peripheral nerves disrupts communication, leading to symptoms such as pain, numbness, and weakness.
The body has natural mechanisms to repair damaged nerve fibers, involving specialized cells called Schwann cells. These cells activate after nerve injury and release growth factors to aid in regeneration. However, this process can be slow or incomplete. Over the past two decades, researchers have sought ways to enhance the body’s ability to heal peripheral nerves.
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) treatments offer a promising alternative to traditional approaches like medications or surgery. PRP is derived from the patient’s own blood and contains a concentrated mix of healing factors, including growth factors and proteins that support tissue repair.
In the case of peripheral neuropathy, PRP treatments may stimulate Schwann cells to release proteins that promote nerve regeneration and protect nerve health. These proteins support the repair of damaged nerve fibers (axons) and may improve nerve function.
Physicians in the licensed Regenexx network use specialized techniques to increase the concentration of growth factors in PRP treatments, tailoring them to each patient’s specific needs. Unlike surgery or medications, PRP treatments work with the body’s natural healing process without the higher risks typically associated with invasive procedures or medication side effects.
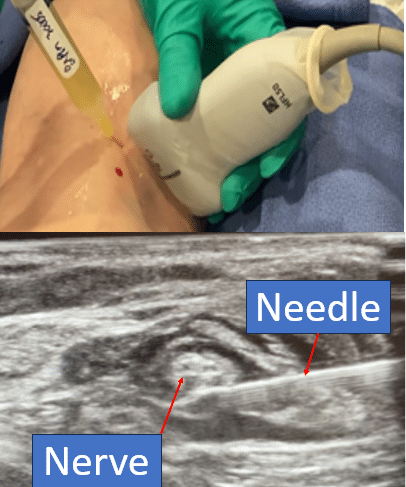
In addition to what is injected, the injection is a highly specialized target treatment under direct visualization with musculoskeletal ultrasound. The procedure is called Hydro-Dissection, where a highly trained doctor uses ultrasound to identify the nerve at the location of entrapment, guides a small needle to the damaged nerve, and injects the platelet or growth-factor injectate around the nerve.
This procedure does two things:
- The fluid injected around the nerve creates space for the nerve to move freely in the soft tissue, “decompressing” or dissecting the nerve away from scar tissue or bony entrapment points or adhesions
- The fluid used is the growth factor-rich injectate, which can stimulate healing effects for the nerve, accelerating nerve repair and allowing the rebuilding and insulation of the nerve!
Signs and Symptoms of Peripheral Neuropathy
Damage to peripheral nerves disrupts the normal transmission of sensory and motor signals, leading to discomfort and impaired function. Common signs and symptoms include:
- Burning pain: A persistent burning sensation, often worse at night, caused by damaged nerves sending incorrect pain signals to the brain.
- Numbness or tingling: Loss of sensation or a prickling feeling, typically starting in the hands or feet, due to damaged nerves’ impaired ability to transmit sensory signals.
- Muscular weakness: Weakness occurs when nerves fail to deliver motor signals necessary for muscle contraction.
- Electric sensations: Sharp, stabbing sensations from disrupted nerve signaling, often described as small electric shocks.
- Localized swelling: Swelling in specific areas without a clear external cause, potentially linked to nerve damage affecting blood flow and fluid regulation.
- Allodynia: Pain from non-painful stimuli, like light touch, occurs when damaged nerves become hypersensitive.
- Hyperalgesia: An exaggerated pain response to normally mild discomfort, resulting from overly sensitive nerve pathways.
Causes of Peripheral Nerve Injuries
Nerve damage can occur suddenly due to acute injuries or develop gradually as a result of chronic conditions. Some of the most common causes include:
- Direct trauma: Blunt force from car accidents or sports injuries can severely damage nerves. Other traumatic events, such as certain surgical procedures, can also result in nerve injury.
- Stretch injuries: Excessive stretching of nerves, usually beyond 5–15% of their normal length, can cause fiber tears. This can happen in high-impact activities where nerves are stretched beyond their normal range.
- Compressive injuries: Nerves can be compressed by swelling, bone spurs, or conditions like carpal tunnel syndrome. Over time, this pressure can irritate and damage nerve fibers.
- Repetitive friction: Continuous friction or repetitive stress on nerves can lead to damage. This is common in people who engage in repetitive manual work, certain sports, or activities like frequent typing.
- Metabolic diseases: Metabolic conditions like diabetes can have systemic effects that damage nerves over time. Diabetic neuropathy is one of the leading causes of peripheral nerve damage, with an estimated half of diabetic patients developing some form of neuropathy.
Other Nerve Conditions Treated by Our Nonsurgical Treatments
The Centeno-Schultz Clinic offers a variety of procedures aimed at helping patients avoid surgeries and epidural steroid injections for treating peripheral neuropathy and related injuries. These advanced treatments harness the patient’s own natural growth factors or bone marrow concentrate, promoting healing and regeneration.
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (Median Neuropathy)
Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) occurs when the tunnel in the wrist narrows, or the median nerve becomes compressed. This condition can cause significant discomfort, with symptoms such as tingling, burning, or numbness in the thumb. At the Centeno-Schultz Clinic, the Perc-CT SR Procedure is employed to alleviate these symptoms and restore functionality.
Cubital Tunnel Syndrome (Ulnar Neuropathy)
Cubital tunnel syndrome is the most common nerve compression issue affecting the upper extremities. It happens when the median nerve is compressed at the elbow, often due to swollen tendons and repetitive movements. At the Centeno-Schultz Clinic, the nerve hydrodissection procedure, combined with PRP or bone marrow concentrate, has shown consistent and promising results.
Brachial Nerve Injuries
The brachial plexus is a network of nerves that extends from the spinal cord through the neck and shoulder, controlling movement and sensation in the arm and hand. Depending on which part of the nerve is affected and the extent of the damage, some individuals may experience full recovery, while others might face ongoing symptoms, like the loss of use or sensation in part of their arm. At the Centeno-Schultz Clinic, tailored regenerative treatments aim to enhance recovery and improve outcomes for those with brachial plexus injuries.
Baxter’s Neuropathy
It is an entrapment syndrome, like carpal tunnel syndrome in your hand. This is an entrapment of a nerve in your foot, right around your heel, on the inside part compressing a branch of your tibial nerve called your inferior calcaneal nerve, and that is the Baxter’s nerve. Now, the inferior calcaneal nerve is the first branch of the lateral plantar nerve, which is a branch off your tibial nerve. It lives between a muscle belly called your abductor hallucis muscle, as well as the medial calcaneal tuberosity, which is a small bump where a common heel spur occurs in the foot.
Read More About Baxter’s NeuropathyPeroneal Nerve Injury
The common peroneal nerve branches behind the knee and this could be irritated from any overuse activity, surgery, instability, or any compression on the outside of the knee. Typically, this will present as pain on the outside of the knee radiating towards the baby toe, the calf, and the lateral shin towards the lateral ankle. What Causes Peroneal Nerve Compression? There are many potential causes of peroneal nerve compression, such as overuse activities, surgery, instability, or any compression on the outside of the knee. Trauma and nerve compression, especially caused by a fractured or dislocated ankle, can all cause injury to the peroneal nerve. Causes include:
Read More About Peroneal Nerve InjuryTrigeminal Neuralgia
Trigeminal Nerve is a cranial nerve that originates in the brain stem. It has 3 main branches (V1, V2, and V3) that innvate the faces. All have sensory fibers except V3 which has both sensory fibers and motor fibers that go to the muscles of the jaw that allow you to chew and talk. Vascular theory = Artery or vein is compressing the Trigeminal Nerve near the pons, or anywhere along the course of the nerve, injuring myelin sheath and causing erratic hyperactive functioning of the nerve! Symptoms typically occur along the V2 or V3 distribution. Symptoms can be variable with moments of extreme pain.
Read More About Trigeminal NeuralgiaRadial Nerve Palsy
The radial nerve is the largest nerve in the upper limb. It starts in the shoulder and travels through the forearm to the back of the wrist. It has nerve fibers from C5, C6, C7, C8, and T1 nerve roots. Radial nerve palsy = damage to the radial nerve which affects the muscles the nerve goes to, creating weakness in those muscles, clinically presenting with wrist drop….the inability to extend the wrist. But the radial nerve innervates many muscles of the upper arm and forearm. When injured, nerve recovery varies widely taking weeks, months, and in some cases years to recover. Addressing the underlying…
Read More About Radial Nerve PalsyThis is not a complete list, so please email, call, or text if you have questions about whether you are a candidate for peripheral neuropathy treatment.
The Procedures of This Treatment
Here is what patients can expect when choosing PRP treatments for peripheral neuropathy:
Before
- Initial evaluation: Before starting PRP treatment, patients undergo a comprehensive evaluation. This includes a review of their medical history and symptoms. A physician in the Regenexx network may perform physical exams and nerve conduction tests to assess the extent of nerve damage.
- Blood draw: PRP is derived from the patient’s own blood. A sample is drawn to begin the preparation process, which involves concentrating the platelets in the next step.
- Treatment planning: Based on the evaluation, the physician will design a personalized PRP treatment plan tailored to the patient’s needs, including determining the concentration of platelets and the injection site.
During
- PRP preparation: The blood sample is processed using specialized equipment to separate and concentrate the platelets into a solution rich in growth factors. Regenexx network physicians utilize an advanced process to customize concentrations based on the patient’s condition.
- PRP injection: Using advanced imaging techniques like ultrasound or C-arm fluoroscopy, physicians in the Regenexx network can guide the PRP injection precisely to the site of the nerve damage for a more targeted delivery of the treatment.
After
- Recovery time: Patients typically experience minimal downtime after the procedure. Most are able to resume light activities within 24 to 48 hours, although it is recommended to avoid strenuous activities for a few days.
- Follow-up appointments: Follow-up visits may be scheduled to monitor progress and determine if additional PRP injections are necessary.
What to Expect
PRP treatments for peripheral neuropathy are non-invasive and require minimal recovery time. After a small amount of blood is drawn, the platelets are concentrated and injected into the damaged nerve area using precise image guidance.
The procedure is relatively short, and patients can typically return to their regular activities soon after. While symptom improvements may begin within a few weeks, optimal results often develop over several months. Physicians in the Regenexx network will provide specific post-procedure care instructions to promote recovery and improve nerve function.
Why Non-Surgical Treatments Are Better
Non-surgical treatments like PRP injections provide several advantages in managing peripheral neuropathy. They may help the body heal naturally and reduce the likelihood of needing more invasive interventions.
- Faster Recovery
Non-invasive treatments like PRP injections typically allow for a faster recovery than surgery. By harnessing the body’s own healing processes, patients may experience symptom relief sooner and can return to their daily routines without the extended recovery period that surgery often requires.
- Reduced Surgical Risks
Surgery for peripheral neuropathy can involve risks such as infection, nerve damage, and extended recovery times. Non-invasive treatments like PRP injections reduce these risks by avoiding the need for incisions or anesthesia.
- Supports Natural Healing
PRP treatments enhance the body’s natural healing mechanisms by using the patient’s own growth factors. This approach targets the source of pain and supports long-term recovery, potentially minimizing the need for medications or surgery.
Centeno-Schultz Clinic’s Other Advanced Procedures for Nerve Repair
In addition to PRP treatments, physicians in the licensed Regenexx network offer advanced, less-invasive therapies designed to promote nerve repair and regeneration. One such procedure is hydro-dissection.
Hydrodissection
Hydrodissection is a technique used to treat nerve entrapments by gently separating nerves from surrounding tissues using a fluid solution. The solution, which may include saline or biologics like PRP, helps reduce pressure on the nerve, improving its function and relieving pain.
Using ultrasound guidance, physicians in the Regenexx network can precisely administer the solution around the affected nerve. This procedure not only reduces compression but also enhances the nerve’s ability to heal, making it a promising option for treating peripheral neuropathy.
Treat Your Nerve Damage Now
If you are experiencing numbness or tingling, or you have been diagnosed with peripheral neuropathy, surgery does not have to be your first option. Contact a physician in the Regenexx network to find out whether interventional orthobiologics may be right for you.
Contact us today to learn how we can help you take the first step toward lasting relief.
Am I a Candidate?
To answer this question, fill out the candidate form below to request a new patient evaluation, and a patient advocate will reach out to you to determine your next steps. Your one-hour, in-office or telemedicine evaluation will be with one of the world’s experts in the field of Interventional Orthopedics.