Cartilage arthroscopic knee surgery is utilized in patients with knee pain who have a reduction in the cartilage on the femoral condyle or tibial plateau.
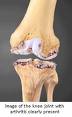
Reduction of cartilage in the knee joint can arise from many sources including osteoarthritis, trauma, degeneration or surgical removal of the meniscus and excessive wear due to biomechanical imbalances.
Cartilage arthroscopic knee surgery can refer to several different types of surgeries. The most common is microfracture surgery in which the surgeon through a scope creates a grid like pattern of small fractures of the knee cartilage that extend into the subchondral bone. Bleeding occurs along with release of stem cells which form a delicate clot. The intended result is to initiate the formation of new cartilage. Unfortunately the cartilage that is formed is fibrocartilage rather than the intial hyaline cartilage which covers the joint. In addition, the fibrocartilage is not as good mechanically as the original hyaline cartilage; it is much denser and isn’t able to withstand the demands of everyday activities as well as hyaline cartilage and is therefore at higher risk of breaking down. Rehabilitation involves following microfracture is typically 6-8 weeks of non-weight bearing followed by extensive physical therapy.
Regenexx uses a patient’s own stem cells to regenerate knee cartilage without the need for surgery or the extensive physical restrictions and rehabilitation associated with microfracture. At Regenexx a patient undergoes a simple x-ray guided needle procedure in which their own stem cells are placed along the area of damage. No anestheis is required. Centeno et al published a study which demonstrated an increase in knee cartilage following stem cell therapy.
