Knee pain affects about 25% of the population (1). The knee joint involves three bones, namely the patella, the femur, and the tibia. Knee pain can be a sign of damage to the ligaments, bones, bursae, or muscle tendons because there are so many structures within the knee joint. In this post, we’ll discuss the symptoms and learn about the treatment options for knee pain.
Where In The Knee Does It Hurt?
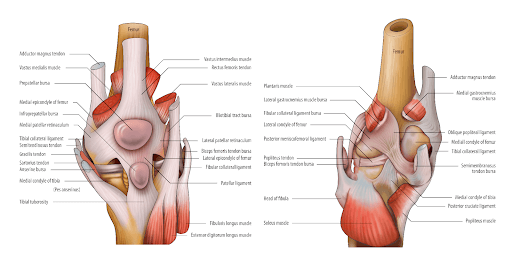
Knee pain can arise from any of the structures in and around the knee joint. There are many muscles, ligaments, tendons, bursae, bones, arteries, nerves, and cartilage that are involved in the knee joint.
The location of the pain and the accompanying symptoms can provide some clue as to the cause of the knee pain and the symptoms. The following is a list of the different parts of the knee that could be causing the pain:
Top Of The Knee
The top of the knee includes the quadriceps tendon and the lower end of the femur. Pain in the top of the knee could indicate damage to these structures.
Outer Knee
The iliotibial band runs on the outside of the knee. Pain in the lateral knee can also point to pathology in the lateral collateral ligament.
Back Of The Knee
Pain at the back of the knee could be due to hamstring injuries, a posterior cruciate ligament tear, a Baker’s cyst, or a meniscus tear.
Knee Cap
The patella, more commonly known as the kneecap, forms the central part of the knee. Pain here could be due to patellar injuries, bursitis, and even tibial fractures.
Limited Range Of Motion
Movement limitations can also help determine the underlying cause of the symptoms and what structures are involved. The following is a list of the limitations of motion and probable causes associated with it:
Unable To Bend Knee
There are several reasons a patient may not be able to bend their knee. One is that the knee is locked and will not unlock. In other cases, joint effusion may prevent knee flexion or the knee pain itself may prevent a patient from bending their knee.
Some of the conditions that prevent the knee from bending include knee bursitis, patellar tendonitis, iliotibial band syndrome, osteoarthritis, or a Baker’s cyst.
Unable To Straighten Knee
Several different knee injuries may limit knee extension. For example, a torn meniscus or cruciate ligament may prevent the knee from straightening. Additionally, an injury to the quadriceps or patellar tendon may mean the knee cannot straighten out as these structures help extend the knee.
Back Of The Knee Feels Tight
Pain or injuries to structures in the posterior knee can make the back of the knee feel tight. For example, hamstrings or calf injuries in the lower extremity can lead to tightness in this area. This is further explained below:
The Hamstrings
Injuries or pain in the hamstrings, such as hamstring tendonitis, can cause posterior thigh pain at the back of the knees. This type of knee pain is usually more pronounced when the knee is bent because the hamstrings muscles are the primary flexors of the knee joint.
The Calves
The posterior knee involves the calf muscles. The calf muscles include the two heads of the gastrocnemius: the medial head, and the lateral head and the soleus. Posterior knee pain can be due to tear or injury to these muscles.
The main role of these muscles is to create traction on the femur causing the knee to bend. If there is a tear or injury to these muscles, then it affects the flexion of the knee and posterior knee tightness and pain.
Painful Sensation In The Knee
The type of pain can also provide a hint about what is causing the knee pain. Here is a list of types of pain and what may be causing it:
Knee Hurts When Stepping On The Stairs
Knee pain while climbing stairs is a sign of two injuries in particular: damage to the patella or the patellar tendon and arthritis of the knee joint. The patellar tendon can be injured from overuse, due to repetitive motions like kneeling and squatting.
Arthritis of the knee joint can cause generalized inflammation ad swelling of the knee which causes limitations of the patella and restricts the joints when stepping on the stairs. Stair climbing involves the patella heavily duringflexion of the knee.
Feeling A Sharp Pain Or Electrical Jolts In The Knees
Sharp shooting pain or electrical jolts within the knee could be due to nerve entrapment of nerves that supplies the knee, muscle imbalances, infection, and muscle tightness. When the nerve is trapped during its course in the muscle or due to an invasive microbe that is affecting the nerve, the nerve responds by sending sharp electrical signals perceived as shooting pain.
Burning Sensation In The Knees
A burning sensation in the knees or feeling as if the knee is on fire could be a sign of gout, infection, bursitis, or even a meniscus injury. The knee might be hot to touch with a significant amount of swelling. The burning sensation or pain is due to the nerves supplying the joint being affected by the infection or injury.
Unstable Knee Or Giving Out
The feeling that the knee is unstable or about to give way can be very telling about the cause of the knee pain.
Below are listed, examples of when an unstable knee can give out and its possible causes.
When Walking
If the knee gives way while walking, it is more than likely due to a ligament injury. This could be damage or injury to the cruciate ligaments or the collateral ligaments.
When Standing Up From Sitting
Pain or instability when standing up from a sitting position are signs of patellofemoral syndrome. This is because the patella is involved. When there is damage to the patella and breakdown of the cartilage under the patella, movement such standing from sitting produces pain and the feeling that the knee may give out.
When Pivoting
The menisci in the knee help prevent the knee from over rotating. The feeling that the knee is unstable while twisting or pivoting can be a sign that there is a meniscus injury.
When Stepping On Stairs
Knee pain and instability while climbing stairs can be due to ligament injury, a meniscus tear, arthritis, or patellar instability. While climbing stairs the entire knee joint is actively playing a role, the laigments, the menisci, and the patella. If the knee is unstable while stepping on the stairs, injury to any of the above can cause knee instability.
Swelling At The Back Of The Knee
Knee pain can be accompanied by swelling in the knee joint. The swelling at the back of the knee can help pinpoint the cause and diagnosis of the knee pain. There are different types of swelling in the knee and different causes for the swelling listed below:
- There Is A Lump
If there is a palpable lump in the back of the knee that moves, it could be a Baker’s cyst. A Baker’s cyst is a fluid-filled cyst that causes pain in the back of the knee, particularly when the knee is bent. There is a localized swelling over the cyst. This pain can also extend to the calf muscles if the cyst grows larger.
- There Is No Lump, Just Swelling
If there is generalized swelling but no lump, this is a sign of joint effusion with joint fluid. This fluid is rich in inflammatory chemicals is being released to repair the main cause of the injury within the joint.
The inflammatory chemicals can cause generalized swelling of the joint and an effusion of fluid. This effusion could be due to an infection, injury, inflammation. or bleeding within the joint and can cause significant knee pain.
Bruising On The Sides Of The Knee
Bruising on the sides of the knee is a visible sign of a localized hematoma or collection of blood. A blow to the knee, a ligament or tendon tear, or a fracture can result in pooling blood in the affected area, leading to bruising on the sides of the knee.
Knee Twitching
Knee twitching can occur due to the nerve that supplies the knee being impinged, muscle spasms, injuries to muscles of the knee, injuries to the back, and also due to overuse injuries of the knee joint.
Numbness Of The Knee
Numbness in or around the knee can occur due to various reasons. For example, compression stockings, radiculitis, diabetic neuropathy, arthritis, and previous surgery on the knee can all affect the nerves in the knee, thereby affecting the sensation of the joint.
Knees Feel Tender
A tender knee or a knee that is painful to the touch can be a symptom of an infection, inflammation due to arthritis, a fracture, or a tendon, cartilage, or muscle tear.
Knee Feels Like It’s About To Pop
The distinct feeling that the knee is about to pop, especially when the knee is flexed while sitting, kneeling or climbing stairs is commonly seen in runners. This happens when there is cartilage damage under the patella. The damage occurs due to overuse.
There is a general tightness across the knee and the pain is exacerbated by motion. The tight feeling as if the knee is about to pop especially during movement is due to increased weight and pressure during activity. However, some symptoms of the knee have specific symptoms that are listed below.
Does It Come With A Sound?
It’s important to identify if the knee pain is accompanied by a sound. Here are some sounds you might hear when there is an injury to the knee and knee pain:
Popping And Clicking In Knee
Popping and clicking in the knee is a sign that something within the knee joint is out of alignment. When the meniscus tears or the tendon snaps, the knee is pulled in the opposite direction by the intact ligament with the torn tendon unable to stabilize and align the knee. Torn ligaments can also cause a clicking sound in the knee along with knee pain.
Grinding Sound When The Knee Moves
Grinding sounds when the knee moves can indicate a tear of the meniscus. It also occurs in osteoarthritis of the knee when there is loss of cartilage and the femur grinds against the tibia, causing severe knee pain.
Do You Have A Previous Knee Condition?
Previous conditions involving the knee can cause chronic knee pain. Some of these conditions are listed below:
- Knee Replacement
About 20% of people who have had a total knee replacement continue to have chronic knee pain (2). This could be due to biological reasons or surgical reasons. The biological causes include increased sensitivity due to long-term arthritis, allergy to the prosthesis, inflammation, or regional pain coming from the hip.
The surgical causes include a localized nerve injury, misalignment, incorrect prosthesis size, or loosening of the prosthesis. Knee pain is a symptom that can persist with partial knee replacement surgery as well. - Old Injury
Old injuries can gradually turn into a condition called post-traumatic arthritis. Immediately after the injury, the joint fluid releases inflammatory mediators which can persist over months or years.
As a result, the joint continues to be inflamed, with symptoms of knee pain, joint effusion, and intra-articular bleeding. This can lead to chronic inflammatory arthritis and long-term knee pain. So long standing injuries with chronic inflammation develop into pos-traumatic arthritis long after the primary injury to the joint. - Past Surgeries
Past knee surgeries can also cause knee pain. For example, a meniscus repair, meniscectomy, ACL reconstruction surgery, microfracture surgery, plica removal surgery, and tendon repair surgery are some of the surgeries that can cause persistent knee pain. This could be due to nerve damage from the surgery or the abnormal healing at the surgical site with fibrous tissue.
Common Causes Of Knee Pain
Since the knee is a complex joint involving many ligaments, muscles, cartilage, and bones, there are a wide variety of causes of knee pain. The common causes of knee pain are outlined below:
- Ligament Injuries
In the knee, there are two primary groups of ligaments that connect the femur with the patella and the tibia: the collateral ligaments and the cruciate ligaments. The collateral ligaments include the medial collateral ligament (located on the inside of the knee) and the lateral collateral ligaments (located on the outside of the knee).
Then there’s the anterior cruciate ligament and the posterior cruciate ligament. They are arranged in the form of a cross and control the back and forth movement of the knee. Any injury or blow to the knee can cause a ligament tear, leading to knee pain. - Meniscal Tears
The knees have C-shaped cartilages called menisci which act as cushions between the femur and tibia. A meniscal tear due to an accident or knee injury or any forceful twisting of the knee can cause severe knee pain within 24 hours.
Meniscus tears vary based on the type of injury and the severity of the knee twist. There are six types of meniscus tears and they all have different treatments. - Arthritis
Arthritis is an inflammatory condition where the joint cartilage breaks down over time, giving rise to knee pain.
There are many types of arthritis that can affect the knee joint including osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, gouty arthritis, and lupus-induced arthritis among others. Arthritic knee pain is primarily due to inflammation and the presence of inflammatory chemicals attacking the joint.
- Bone Fracture
Fracture of the femur, patella, or tibia can cause knee pain. These fractures could be open or closed (that is, with or without breakage of the skin respectively). They could be displaced where the bone has moved out of place or nondisplaced where the broken pieces of bone stay in place. Fractures can cause immediate and severe knee pain at the time of the injury.
- Muscle Injuries
There are various large groups of muscles that insert and attach to the knee joint. This includes the quadriceps, the hamstrings, and the calf muscles. Muscle sprains, tears, muscle tightness, and even hypertrophied muscles can all cause knee pain due to the active role these muscles play in the movement of the knee joint.
- Overuse Of The Knee
Overuse of the knee from repeated falls or repetitive motions like kneeling, squatting, and bending can irritate the bursae of the knee and give rise to bursitis. This inflammation of the bursae can also cause knee pain.
Avoiding Knee Surgery
It’s not necessary to have knee surgery for all knee conditions. There are many knee conditions that do very well with conservative therapy, including physical therapy and regenerative medicine.
Before you decide to have surgery, it might be worth considering these alternative options for knee pain treatment. At Centeno-Schultz Clinic, we offer all these therapies as an alternative to surgery.
Would you like to learn about how to avoid knee surgery? Download our ebook through this link!
References:
- Bunt CW, Jonas CE, Chang JG. Knee Pain in Adults and Adolescents: The Initial Evaluation. Am Fam Physician. 2018;98(9):576-585.
- Wylde V, Beswick A, Bruce J, Blom A, Howells N, Gooberman-Hill R. Chronic pain after total knee arthroplasty. EFORT Open Rev. 2018;3(8):461-470. Published 2018 Aug 16. doi:10.1302/2058-5241.3.180004

